
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.
1. Introduction to plate heat exchanger
The plate heat exchanger is a new type of high efficiency heat exchanger which is assembled from a series of metal sheets with a certain corrugated shape. A thin rectangular channel is formed between the various sheets, and heat exchange is performed through the half sheets. Compared with the conventional shell-and-tube heat exchanger, the heat transfer coefficient is much higher under the same flow resistance and pump power consumption, and there is a tendency to replace the shell-and-tube heat exchanger within the applicable range.
The types of plate heat exchangers are mainly frame type (detachable type) and brazed type. The plate form mainly consists of herringbone corrugated plate, horizontal straight corrugated plate and nodular plate.
1.1 Basic structure of plate heat exchanger
The plate heat exchanger is mainly composed of two parts: a frame and a plate.
Sheets Sheets made of various materials are pressed into corrugations of various shapes by various types of abrasive tools, and angular holes are formed in the four corners of the sheet for the flow path of the medium. The periphery of the plate and the corner hole are sealed with a rubber gasket.
The frame is composed of a fixed pressing plate, a movable pressing plate, upper and lower guide bars, and clamping bolts.
The plate heat exchanger is formed by superimposing the plates in the middle of the fixed pressing plate and the movable pressing plate, and then clamping them with clamping bolts.
1.2 Characteristics of plate heat exchanger (comparison of plate heat exchanger and shell-and-tube heat exchanger)
a. High heat transfer coefficient Because different corrugated plates are inverted with each other, a complicated flow path is formed, so that the fluid flows in a three-dimensional flow in the flow path between the corrugated plates, and can be generated at a low Reynolds number (generally Re=50-200). Turbulent flow, so the heat transfer coefficient is high, generally considered to be 3 to 5 times the shell-and-tube type.
b. The logarithmic mean temperature difference is large, and the terminal temperature difference is small. In the shell-and-tube heat exchanger, the two fluids flow in the tube and shell processes respectively, which is generally a cross-flow flow, and the logarithmic mean temperature difference correction coefficient is small, and the plate type The heat exchangers are mostly cocurrent or countercurrent flow modes, and the correction coefficient is usually about 0.95. In addition, the flow of cold and hot fluids in the plate heat exchanger is parallel to the heat exchange surface and there is no bypass flow, thus making the plate heat exchanger The temperature difference at the end of the device is small, the heat exchange for water can be lower than 1 ° C, and the shell-and-tube heat exchanger is generally 5 ° C.
c. The small-plate heat exchanger covers a compact structure, and the heat exchange area per unit volume is 2~5 times that of the shell-and-tube type. It is not the same as the shell-and-shell type, and the inspection and repair place for the extracted tube bundle is reserved. The heat exchange capacity, the plate heat exchanger covers an area of about 1/5~1/10 of the shell-and-tube heat exchanger.
d. It is easy to change the heat exchange area or process combination. As long as several plates are added or reduced, the purpose of increasing or decreasing the heat exchange area can be achieved. By changing the plate arrangement or replacing several plates, the required process combination can be achieved. To adapt to the new heat exchange conditions, the heat transfer area of the shell-and-tube heat exchanger is almost impossible to increase.
e. The thickness of the light-weight plate heat exchanger is only 0.4~0.8mm, while the thickness of the heat exchange tube of the shell-and-tube heat exchanger is 2.0~2.5mm, and the shell-and-shell type is more than the plate heat exchanger. The frame is much heavier, and the plate heat exchanger is generally only about 1/5 of the shell-shell weight.
f. The price is low and the same material is used. Under the same heat exchange area, the price of the plate heat exchanger is about 40%~60% lower than that of the shell and tube type.
g. The heat transfer plates for making convenient plate heat exchangers are stamped, highly standardized, and can be mass-produced. Shell-and-tube heat exchangers are generally hand-made.
h. Easy to clean the frame type plate heat exchanger As long as the compression bolt is loosened, the plate bundle can be loosened and the plate can be removed for mechanical cleaning, which is very convenient for the heat exchange process of the equipment to be cleaned frequently.
i. Heat Loss Small plate heat exchanger Only the outer plate of the heat transfer plate is exposed to the atmosphere, so the heat loss is negligible and no heat preservation measures are required. The shell-and-tube heat exchanger has a large heat loss and requires a heat insulating layer.
j. The smaller capacity is 10%~20% of the shell-and-tube heat exchanger.
k. The pressure loss per unit length is large due to the small gap between the heat transfer surfaces, and the heat transfer surface has irregularities, so the pressure loss is larger than that of the conventional smooth tube.
l. It is not easy to scale. Because it is fully turbulent inside, it is not easy to scale. The fouling coefficient is only 1/3~1/10 of the shell-and-tube heat exchanger.
m. The working pressure should not be too large, the medium temperature should not be too high, it is possible to leak the plate heat exchanger with a gasket seal, the working pressure should generally not exceed 2.5MPa, the medium temperature should be below 250 °C, otherwise it may leak.
n. Easy to block because the channel between the plates is very narrow, generally only 2~5mm. When the heat exchange medium contains large particles or fibrous substances, it is easy to block the passage between the plates.
1.4 Plate heat exchanger application
a. Refrigeration: Used as a condenser and evaporator.
b. HVAC: intermediate heat exchangers used in boilers, intermediate heat exchangers in high-rise buildings, etc.
c. Chemical industry: soda ash industry, ammonia synthesis, alcohol fermentation, resin synthesis cooling, etc.
d. Metallurgical industry: heating or cooling of aluminate mother liquor, cooling of steelmaking process, etc.
e. Machinery industry: various quenching liquid cooling, reducer lubricating oil cooling, etc.
f. Power industry: high-voltage transformer oil cooling, generator bearing oil cooling, etc.
g. Paper industry: heat recovery in bleaching process, heating of washing slurry, etc.
h. Textile industry: cooling of viscose aqueous solution, boiling nitrocellulose cooling, etc.
i. Food industry: juice sterilization cooling, animal and vegetable oil heating and cooling.
j. Grease process: The soap base is dried at normal pressure, and the various process liquids are heated or cooled.
k. Central heating: heating in the waste heat of the thermal power plant, heating the bath water.
l. Others: petroleum, medicine, ship, seawater desalination, geothermal utilization.
1.5 should pay attention to the selection of plate heat exchanger
1.5.1 Board type selection
The plate type or corrugated type should be determined according to the actual needs of the heat exchange occasion. For the case where the flow rate is large and the pressure drop is small, the plate type with low resistance should be selected, and the plate type with large resistance should be selected. Depending on the fluid pressure and temperature, it is determined whether the detachable or brazed type is selected. When determining the plate type, it is not suitable to select the plate with too small a single plate area, so as to avoid too many plates, the flow velocity between the plates is too small, and the heat transfer coefficient is too low. This problem should be paid more attention to the larger heat exchanger.
1.5.2 Process and runner selection
The process refers to a set of parallel flow channels in a plate heat exchanger with the same direction of motion, and the flow channel refers to a medium flow channel composed of two adjacent plates in the plate heat exchanger. In general, several flow passages are connected in parallel or in series to form different combinations of cold and heat medium passages.
The process combination should be calculated based on heat transfer and fluid resistance and determined to meet process conditions. Try to make the convective heat transfer coefficient in the cold and hot water flow channels equal or close, so as to get good heat transfer effect. The heat transfer coefficient obtains a larger value because the convective heat transfer coefficients on both sides of the heat transfer surface are equal or close. Although the flow rates between the plates of the plate heat exchanger are not equal, the calculation is based on the average flow rate in the calculation of heat transfer and fluid resistance. Since the "U"-shaped single-flow nozzle is fixed on the pressing plate, the disassembly and assembly is convenient.
1.5.3 Pressure drop check
In the design and selection of the plate heat exchanger, there is a certain requirement for the pressure drop, so it should be checked. If the check pressure drop exceeds the allowable pressure drop, the design selection calculation must be repeated until the process requirements are met.
return
Plate heat exchanger
Overview
The BR type plate heat exchanger produced by our factory has high heat exchange efficiency, small material flow resistance loss, compact structure, sensitive temperature control and operation.
It has the characteristics of large elasticity, convenient assembly and disassembly, long service life, etc. It is the advanced energy-saving heat exchange equipment of the domestic Zui.
The plate heat exchanger products produced by our factory can process a wide range of materials, from ordinary industrial water to high-viscosity liquids, from hygienic liquids and pharmaceutical materials with high hygienic requirements to acid and alkali liquids with certain corrosive properties. From a liquid material containing granule powder to a suspension liquid containing a small amount of fiber, it can be treated with a plate heat exchanger. Can be used for heating, cooling, evaporation, condensation, sterilization, heat recovery and other occasions. Such as cooling generators and rectifiers circulating; for mechanical lubricants such as metallurgical mines; sterilization of hydraulic stations, egg liquids, edible oils, sterilization of beer and wine; waste heat recovery in the textile industry and paper industry; Collect condensed water, concentrate heating; steam reforming water; intermediate heat transfer in boiler deoxygenation system. It has been widely used in industrial sectors such as metallurgy, mining, petroleum, chemical, electric power, medicine, food, chemical fiber, textile, paper, ship and central heating.
Structural principle
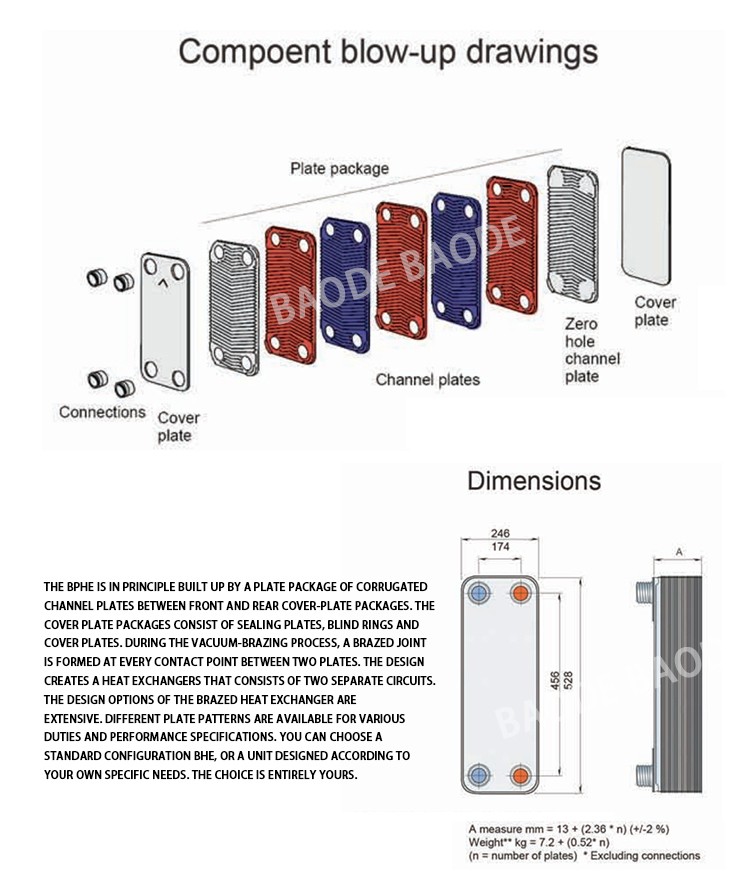
The detachable plate heat exchanger is formed by a plurality of stamped corrugated sheets at regular intervals, surrounded by gaskets, and pressed by a frame and a compression screw. The four corner holes of the plates and the gasket form a fluid. The piping and the collecting tube are simultaneously separated from each other reasonably, so that they flow in the flow paths on both sides of each of the sheets, and heat exchange is performed through the sheets.
Design features of plate heat exchangers
1. High efficiency and energy saving: its heat transfer coefficient is 3000~4500kcal/m2·°C·h, which is 3~5 times higher than the thermal efficiency of shell-and-tube heat exchanger.
2. Compact structure: the plate heat exchanger plates are closely arranged. Compared with other heat exchanger types, the plate heat exchanger has less floor space and space occupation, and the plate heat exchanger with the same heat exchange capacity is only the tube. 1/5 of the shell heat exchanger.
3. Easy to clean and disassemble: The plate heat exchanger clamps the clamping plate by clamping bolts, so it is easy to disassemble and install, and can be opened and cleaned at any time. At the same time, due to the smooth surface, the turbulence is high and it is not easy to scale.
4, long service life: plate heat exchanger is made of stainless steel or titanium alloy plate, can resist a variety of corrosive media, rubber pads can be replaced at will, and can be easily installed, disassembled and repaired.
5. Adaptability: The plate heat exchanger plate is a separate component, which can be increased or decreased according to requirements, and has various forms; it can be applied to various requirements of different processes.
6. Without liquid, the plate heat exchanger sealing groove is provided with a liquid discharge channel, and various media will not collide. Even if leakage occurs, the medium is always discharged outward.
Plate heat exchanger application range
Plate heat exchangers have been widely used in metallurgy, mining, petroleum, chemical, electric power, medicine, food, chemical fiber, paper, textile, ship, heating and other departments, can be used for heating, cooling, evaporation, condensation, sterilization, waste heat Recycling and other situations
chemical industry
Production of titanium oxide, alcohol fermentation, ammonia synthesis, resin synthesis, rubber production, cooling of phosphoric acid, cooling of formalin, alkali carbon industry, electrolysis of alkali.
iron industry
Cool the quenching oil, cool the plating solution, cool the reducer lubricant, cool the rolling mill, and draw the machine coolant.
Heating and cooling of the aluminate mother liquor in the metallurgical industry, cooling the sodium aluminate, and cooling the aluminum alloy rolling mill lubricant.
Various quenching liquids in the mechanical manufacturing industry are cooled, cooling presses, industrial machine lubricating oils, and engine oils are heated.
Food industry salt, dairy, soy sauce, vinegar sterilization, cooling, animal and vegetable oil heating, cooling, beer production, beer, wort heating and cooling, sugar, gelatin concentration, sterilization, cooling, manufacturing sodium glutamate.
The textile industry heat recovery of various waste liquids, cooling of boiling phosphating fibers, cooling of viscose liquid, cooling of acetic acid and acid anhydride, cooling of aqueous alkali solution, heating and cooling of viscose.
The paper industry cools black water, bleaches salt, lye heating, cooling, heat recovery of cellophane waste liquid, heating and cooking acid, cooling sodium hydroxide aqueous solution, recovering waste paper of bleached sheet, condensing of exhaust gas, preheating Concentrate pulp-like waste.
Central heating, thermal power plant waste heat district heating, heating domestic water, boiler district heating
The oil industry heats and cools synthetic detergents, heats whale oil, cools vegetable oil, cools sodium hydroxide, and cools glycerin and emulsified oil.
Power industry generator shaft pump cooling, transformer oil cooling.
Marine diesel engine, central cooler, unloader water cooler, piston cooler, lube oil cooler, preheater, desalination system (including multi-stage and single-stage)
Other medicines, petroleum, ceramics, glass, cement, geothermal utilization, etc.
September 21, 2023
September 06, 2023
Contactar proveedor
September 21, 2023
September 06, 2023

Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.

Fill in more information so that we can get in touch with you faster
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.